device tree
This is my study note of device tree.
基本知识
基本名词
- DT: 设备树
- FDT(Flatten device tree): 开发设备树
- dts: 设备树源码
1
路径:/linux/kernel/arch/arm(or arm64)/boot/dts
- dtsi:通用的设备树源码(重复的部分)
- dtb:编译设备树后得到的文件
- dtc:编译设备树的编译器
编译设备树
1 | dtc路径:/linux/kernel/scripts/dtc |
- 编译命令
1
dtc -I dts -O dtb -o xxx.dtb xxx.dts
- 反编译命令
1
dtc -I dtb -O dts -o xxx.dts xxx.dtb
语法
版本号
1
/dts-v1/;
结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7/{
// 根结点名为“/”
led:led@19121
{
// 标签(别名):名称@设备地址
};
}属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>; // 用于描述子节点的地址和长度信息
child_node
{
reg = <0x02 0x01>; // 描述地址信息,比如寄存器地址(地址在前,长度在后)
};
status = "" // 属性值为字符串,描述设备状态,有"okay disabled fail fail-sss(sss表示错误内容)"四种状态
compatiable = " "; // 用于与驱动进行匹配,匹配成功后会执行驱动的probe
model = " "; // 用来描述一些信息,比如设备名字等
device_type = "memory"; // 只用于声明cpu结点或memory结点自定义属性
1
属性名 = <>; // 自定义属性名和参数
特殊结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10aliases // 用于定义别名,例如mmc0是&sdmc0的别名,适合排序定义别名
{
mmc0 = &sdmc0;
serial0 = "/simple@125/serial@5455";
};
chosen // 用于uboot给内核传递参数,重点是bootargs参数,chosen结点必须是根节点的子节点
{
};控制器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14gpio-controller; // GPIO控制器
#gpio-cells = <x>; // 表示后续使用gpio时需要输入x个值
ngpios = <x>; // 表示有x个gpio可以使用
gpio-line-names = " "," "; // x个gpio的名字
gpio-reserved-ranges=<m n>; // 保留的gpio,m为起始,n为长度
gpio-ranges = <&x m n q>; // 把n后q个gpio映射到m后q个gpio上
intertrrupt-controller; // 中断控制器
#interrupt-cells = <x>; // 表示后续调用interrupts时需要输入x个值
interrupt-parent = <&结点名> // 引用某个结点,如果当前结点没有指明引用的结点,则使用当前结点的父节点所引用的结点
interrupts = <x x> // 根据cells来确定输入的参数,确定管脚、中断方式等
interrupt-extended = <&结点1 x x>, <&结点2 x x>; // 表示引入多组中断时钟
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13时钟分为生产者和消费者:
1.生产者
#clock-cells = <x>; // x为0时表示只有一路时钟输出,大于等于1时表示多路时钟输出
clock-ouput-names = "x", "x"; // 输出时钟名字
clock-frequency = <x>; // 指定时钟大小
assigned-clocks = <&x a>,<&y b>;
assigned-clock-rates=<m>,<m>; // assign-clocks和assigned-clock-rates一般成对使用,m表示a,b对应的时钟大小
clock-indices = <>,<>; // 用于指定clock-output-names的索引号
assigned-clock-parents = <&x m>; // 用于设置时钟的父时钟
2.消费者属性
clocks = <& x>; // 用于指定时钟源
clocks-names = " "; // 用于指定时钟名字CPU结点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
121.cpus结点
cpu的全部布局在此结点下描述
2.cpu-map结点
主要用在描述大小核架构处理器中,cpu-map结点的父节点必须是cpus结点,子节点必须是一个或者多个cluster和socket结点。
3.socket结点
描述CPU插槽,主板上有几个CPU插槽就有几个socket结点。socket的子节点必须是一个或者多个cluster结点,socket结点的命名方式必须是socketN,N=0,1,2...
4.cluster结点
用于描述CPU的集群,cluster结点的命名方式必须是clusterN,子结点必须为一个或者多个cluster结点或者多个core结点。
5.core结点
用来描述一个cpu,如果只有一个cpu则,core节点就是cpus结点的子节点。
6.thread结点
用于描述处理的线程。pinctrl设置复用关系
1
2
3
4
51.客户端
pinctrl-names = " "; // 表示设备的状态
pintrl-0 = <&pintrl_hog_1>; // 表示第0个状态对应的配置
2.服务端
根据不同厂商进行不同配置
dtb部分
dtb文件格式
dtb文件分为四个部分:
- 头部
- 内存阅读块
- 结构块
1
2
3
40x00000001表示属性开始
0x00000002表示结点结束
0x00000003表示结点开始
0x00000009表示根结点结束 - 字符串块
1
00表示一个字符串的结束。
- 自由空间(不一定存在,用于内存对齐)

1 | 其中,magic一定是0xd00dfeed |
dtb展开为device_node
设备树传递给内核的流程: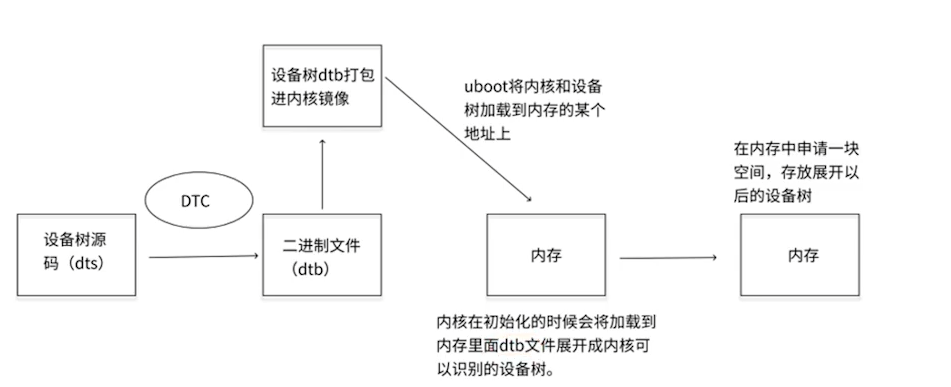
- device_node结构体
1
位于include/linux/of.h的头文件中
- device_node转换成platform_device
1
2
3
4
5并不是所有结点都会被转换,只有满足要求的结点被转换。被转换的结点可以在:"sys/bus/platform/devices"下查看。
转换规则:
1.根节点下包含compatiable属性的子节点
2.节点中compatiable属性包含simple-bus、simple-mfd、isa其中之一的结点下包含compatiable属性的子节点。
3.如果结点的compatiable属性包含arm、primecell值,则对应的结点不会被转换
of操作函数
结点查找
- of_find_node_by_name 通过结点名字查找指定结点
- of_find_node_by_path 通过结点路径查找结点
- of_find_compatible_node 通过compatiable属性查找指定的结点
- of_find_matching_node_and_match 通过compatiable属性列表查找指定结点
- of_get_pareny 获取指定结点的父节点
- of_get_next_child 查找子节点,第二个参数设置为NULL的话,从第一个结点开始
属性查找
- of_find_property 查找节点下指定的属性
- of_property_count_elems_of_size 获取属性中元素的数量
- of_property_read_u32_index 从指定的属性中获取指定标号的u32类型的数据
- of_property_read_u64_index 从指定的属性中获取指定标号的u64类型的数据
- of_property_read_variable_u8_array 读取数组函数
- of_property_read_variable_u16_array 读取数组函数
- of_property_read_variable_u32_array 读取数组函数
- of_property_read_variable_u64_array 读取数组函数
- of_property_read_string 读取字符串函数
ranges属性
1 | 1.ranges = <child-bus-address parent-bus-address len>; |
中断操作
- irq_of_parse_and_map 从interrupts属性中获取到对应的中段号
- irqd_get_trigger_type 从中断属性中获取对应的中断标志
- irq_get_irq_data 返回irq_data结构体
- platform_get_irq 获取中断号
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 风声向寂!
评论
ValineDisqus



